RAID 50 vs. RAID 5 – Which One Offers Better Performance and Data Protection?
Achieving the optimal balance between performance, speed, and data protection is a critical consideration for businesses and tech enthusiasts alike. Two RAID configurations that often come under scrutiny in this context are RAID 5 and RAID 50. RAID 5, known for its efficient use of storage and reliable data security, is a favorite in environments where read-heavy performance is key. On the other hand, RAID 50 combines the benefits of RAID 5 with the added advantages of striping, promising enhanced speed and a robust mechanism against data loss.
This article delves into a comparative analysis of RAID 5 and RAID 50, elucidating the nuances of their performance metrics, speed capabilities, and data protection features. By exploring these aspects, we aim to equip you with a clear understanding of which RAID configuration might best suit your data storage needs.
Understanding RAID 5 and RAID 50 – How They Work
What Is RAID 5?
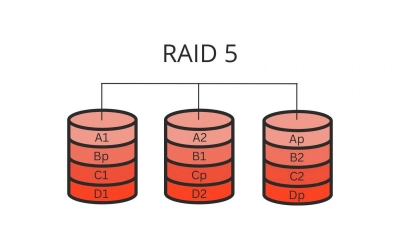
RAID 5 is a popular RAID configuration that utilizes block-level striping with a single parity block distributed across all drives in the array. This approach effectively spreads both data and parity information, allowing the system to rebuild missing information in the event of a single drive failure. The ability to survive the loss of one drive without significant downtime or data loss offers a reliable safeguard, making RAID 5 an attractive choice for businesses and personal use where keeping data accessible and safe is a priority. Additionally, RAID 5 delivers a balanced blend of performance and storage efficiency, providing adequate read speeds and decent write speeds while maximizing the available storage capacity, as only one drive's worth of storage is used for parity.
What Is RAID 50?
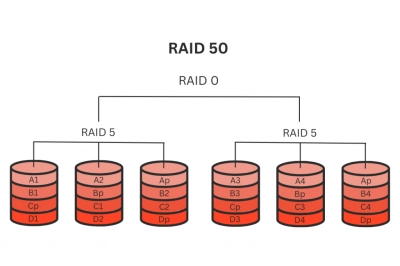
RAID 50 takes the reliability and efficiency of RAID 5 to a higher level by integrating it with RAID 0 striping. Essentially, RAID 50 consists of multiple RAID 5 arrays that are themselves striped in a RAID 0 configuration. This combination significantly enhances both performance and data protection. With RAID 50, not only can multiple drives fail across different RAID 5 sets without causing total data loss, but the system also benefits from elevated read and write speeds. The RAID 0 layer introduces faster data access by spreading the I/O load across the drives, making RAID 50 particularly well-suited for environments where high-speed data processing, sizable storage capacities, and robust redundancy are essential. However, this configuration requires more drives to implement, meaning that while the initial investment is higher, the gains in speed and fault tolerance can be considerable, especially in enterprise-level applications.
Tip: what is a RAID controllerRAID 50 vs. RAID 5 – Key Differences
Performance Comparison – Speed and Efficiency
RAID 50 achieves faster read and write speeds thanks to its incorporation of RAID 0 striping across multiple RAID 5 arrays. This configuration allows for enhanced data throughput, which is especially beneficial in environments requiring high-speed processing and large data volumes. In contrast, RAID 5 tends to have slower write speeds due to the overhead from parity calculations. While reads remain efficient, the time taken to compute and write parity can slightly reduce the overall speed, making RAID 5 less optimal for tasks that demand rapid write access.
Fault Tolerance and Data Protection
RAID 5 provides a solid level of fault tolerance by being able to withstand a single drive failure. This is sufficient for many applications where the probability of multiple simultaneous drive failures is low. However, RAID 50 elevates this protection by enabling the array to tolerate multiple drive failures, as long as they do not occur within the same RAID 5 set. This added layer of security makes RAID 50 particularly appealing in critical environments where data redundancy and availability are paramount.
Storage Efficiency and Cost Considerations
From a storage efficiency standpoint, RAID 5 is quite efficient, permitting maximum usable storage while maintaining only minimal redundancy. This makes it cost-effective, especially when working with a limited number of drives. On the other hand, RAID 50's increased fault tolerance comes at the cost of reduced total usable capacity, as more drives are required not just for storage but also for maintaining additional redundancy. Consequently, RAID 50 involves higher initial costs due to the necessity for more hardware.
Best Use Cases for RAID 50 and RAID 5
RAID 5 is particularly well-suited for general-purpose storage solutions where moderate redundancy and efficiency are adequate. It's a great fit for small to medium-scale applications where budget constraints are as important as maintaining a reasonable level of data protection. Alternatively, RAID 50 is ideal for performance-heavy workloads that demand both high-speed access and enhanced fault tolerance. This makes RAID 50 the preferable choice for enterprise environments or applications that cannot afford downtime, such as those involving financial transactions or large database operations.
RAID 50 vs. RAID 5 – Which One Should You Choose?
When to Use RAID 5
RAID 5 is ideal for small to mid-sized businesses where the number of drives is limited, yet reliable data storage is needed. This configuration is well-suited for backup servers and general storage purposes, providing an economical balance of performance and redundancy without significant complexity or hardware cost.
When to Use RAID 50
RAID 50 is best suited for enterprises that require both high speed and robust redundancy. It excels in environments where virtualization, databases, and high-speed applications are prevalent. The combination of speed from RAID 0 and the fault tolerance of RAID 5 make RAID 50 a preferred choice for demanding workloads and critical data operations.
RAID 50 vs. RAID 5 – Decision Table
| Criteria | RAID 5 | RAID 50 |
| Performance - Speed and Efficiency | Slower writes due to parity calculations | Faster read/write speeds due to RAID 0 striping |
| Fault Tolerance and Data Protection | Can survive one drive failure | Can tolerate multiple failures across different RAID 5 arrays |
| Storage Efficiency and Cost | Maximizes usable storage with minimal redundancy | Requires more drives, reducing total usable capacity |
| Best Use Cases | Suitable for general-purpose storage with moderate redundancy needs | Best for performance-heavy workloads requiring fault tolerance |
RAID Failures and Data Recovery – What Happens When a Drive Fails?
Risks of Data Loss in RAID 5 and RAID 50
In a RAID 5 setup, the main risk of data loss occurs if a second drive fails before the array can be fully rebuilt following an initial drive failure. This creates a window of vulnerability where the entire data set can become inaccessible, emphasizing the importance of a speedy recovery process. RAID 50 offers improved redundancy by distributing data and parity more broadly across the array, yet it is still susceptible to specific failure scenarios. For example, multiple drive failures within the same RAID 5 sub-array could lead to significant data loss or corruption, thereby necessitating careful monitoring and regular maintenance.
RAID Recovery with DiskInternals RAID Recovery™
DiskInternals RAID Recovery™ provides a comprehensive solution for recovering data from failed RAID 5 and RAID 50 arrays. Here’s a step-by-step guide to effectively utilizing this tool:
- Connect Drives: Ensure all drives from the RAID array are connected to a working computer.
- Install and Launch: Download and install DiskInternals RAID Recovery™ on your system. Launch the software once installed.
- Automatic Detection: The software automatically detects RAID parameters. Use this feature to reconstruct the array accurately.
- Scan for Data: Initiate a scan of the RAID array to locate and identify recoverable files and fragments.
- Preview and Recover: Once the scan is complete, you can preview the files to ensure integrity and recover the desired data to a secure location.
DiskInternals RAID Recovery™ reconstructs damaged RAID configurations, facilitating the recovery of files even when logical damage occurs, thus providing peace of mind in the face of potential data loss. Should you need more guidance on RAID recovery options, feel free to ask!
Note: RAID 5 rebuild timeReady to get your data back?
To start RAID 50, RAID 5 recovery, press the FREE DOWNLOAD button to get the latest version of DiskInternals RAID Recovery® and begin the step-by-step recovery process. You can preview all recovered files absolutely for free. To check the current prices, please press the Get Prices button. If you need any assistance, please feel free to contact Technical Support. The team is here to help you to recover data from RAID drive!
Conclusion – RAID 50 vs. RAID 5, Which One Wins?
When deciding between RAID 5 and RAID 50, the choice fundamentally hinges on your specific needs and priorities. RAID 5 stands out as a cost-effective solution, delivering reliable redundancy without the necessity for extensive resources. It's a compelling choice for general storage scenarios where moderate performance and redundancy are sufficient.
On the flip side, RAID 50 offers the performance edge with enhanced speed and resilience, making it particularly suited for high-speed applications, such as virtualization and enterprise databases that demand robust fault tolerance and rapid access times. This configuration is ideal for environments that cannot afford latency or data downtime.
Regardless of the RAID level chosen, it's crucial to always have a robust data recovery solution like DiskInternals RAID Recovery™ in place, ensuring that you are prepared to tackle any unforeseen failures and can rebuild RAID array without losing data.
FAQ
Is RAID 50 faster than RAID 5?
RAID 50, also known as RAID 5+0, combines distributed parity (RAID 5) with striping (RAID 0). It requires a minimum of six drives. This RAID level offers better write performance, increased data protection and faster rebuilds than RAID 5.
What is RAID 5 downside?
RAID 5 data restoration (rebuild time) may take longer depending on the size of the disk that needs to be restored. It also depends on the load on the array as well as the speed of the controller. If two drives fail, data is lost and decreased write performance is due to real-time parity calculations.
What is span in RAID 50?
Spanning is a term used to describe the way in which RAID levels 10, 50, and 60 are constructed from multiple sets of basic, or simple RAID levels.
