RAID 6 Drive Failure Tolerance: How Many Drives Can Fail?
RAID 6, a prominent configuration in the world of redundant array of independent disks (RAID), offers robust protection against data loss. By distributing data and parity information across multiple drives, RAID 6 provides a safeguard against hardware failures. A crucial aspect of this setup is its failure tolerance — the ability of the system to withstand drive failures without data loss.
This article delves into RAID 6's unique architecture, exploring how many drives can fail while still maintaining data integrity and system functionality. We will examine the technical principles behind RAID 6 and highlight why it's a preferred choice for those seeking resilience in their storage solutions.
Understanding RAID 6 Architecture
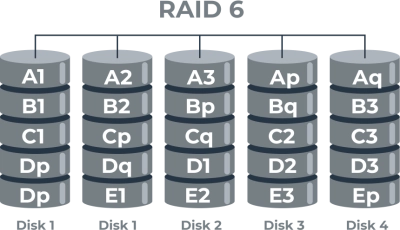
RAID 6 is renowned for its ability to provide high levels of data redundancy and fault tolerance. It achieves this through a combination of innovative techniques that make it a versatile choice, particularly for environments where data loss is not an option.
Dual Parity Mechanism
At the heart of RAID 6 lies its dual parity system, a sophisticated approach to data protection. This mechanism allows for two independent parity calculations to be stored across the array of drives, enabling RAID 6 to survive the simultaneous failure of up to two drives. By using additional parity bits, RAID 6 can reconstruct data from both failed drives, ensuring continuity and preventing data loss even in challenging scenarios. This dual parity system is a key differentiator from other RAID levels, such as RAID 5, which can only handle a single drive failure.
Minimum Drive Requirements
To implement RAID 6, a minimum of four drives is required. This configuration ensures that there are enough drives to hold both data and the necessary parity information. While the minimum setup provides the basic level of redundancy, adding more drives increases the array's storage capacity and enhances its overall redundancy. With each added drive, the RAID 6 array can store more data while maintaining the ability to withstand two drive failures. Thus, expanding the number of drives not only boosts storage potential but also offers increased data security and reliability.
Drive Failure Scenarios in RAID 6
RAID 6 is designed to be a resilient storage solution, providing peace of mind through its ability to handle unexpected drive failures. Understanding its tolerance to such failures is crucial for maximizing its potential.
Tolerance to Drive Failures
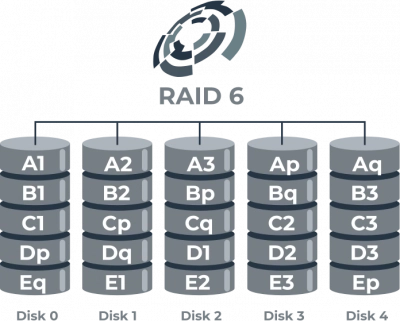
RAID 6's defining feature is its ability to withstand up to two simultaneous drive failures without data loss. This robust tolerance is due to its dual parity system, which ensures that data can be reconstructed even when two drives are compromised. However, if a third drive were to fail before the first two failures are remedied, the RAID 6 array would encounter data loss, as it exceeds the system's redundancy capability.
RAID 6 with Four Drives: Failure Implications
When RAID 6 is configured with the minimum four drives, it sets the baseline for data protection. In this setup, data and parity are distributed across all four drives, allowing the system to survive up to two drive failures. Despite the minimal configuration, the core guarantee of RAID 6 remains unchanged: two drives can fail without impacting data integrity. This assurance makes RAID 6 with four drives a reliable choice for entry-level redundancy.
RAID 5 with Six Drives: Failure Implications
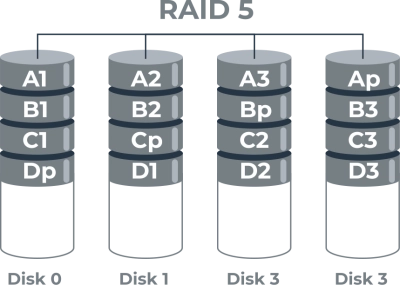
Comparatively, RAID 5 offers different failure tolerance characteristics, even when configured with more drives. In a RAID 5 setup with six drives, the array is capable of surviving only a single drive failure. Regardless of having more total drives compared to a four-drive RAID 6 configuration, once a second drive fails in RAID 5, data loss occurs. This limitation highlights the benefits of RAID 6's dual parity, which provides superior protection over RAID 5's single-parity approach. Thus, RAID 6 is often favored in scenarios requiring greater resilience and reliability. Learn more on RAID 6 vs RAID 5!
Data Recovery in RAID 6
RAID 6 offers robust protection against drive failures, but ensuring data integrity goes beyond just relying on its architecture. Effective data recovery strategies are essential in maintaining optimum performance and safeguarding data.
Importance of Regular Monitoring and Maintenance
Proactive monitoring is key to identifying potential drive issues before they lead to failures. By regularly checking drive health and performance, you can detect anomalies early and take preventive measures to mitigate risks. Implementing a schedule for routine drive checks and ensuring that all system components are functioning correctly can significantly reduce the likelihood of unexpected drive failures. Regular maintenance practices — such as updating firmware, cleaning physical components, and maintaining optimal operating conditions — also play a crucial role in prolonging the life of the drives and the RAID array as a whole.
Utilizing DiskInternals RAID Recovery™ Software
In the event of a drive failure, having reliable data recovery tools is vital. DiskInternals RAID Recovery™ is a powerful software solution designed specifically to assist in data retrieval from RAID environments, including RAID 6. It offers a range of features tailored to meet the unique challenges of RAID data recovery, such as automatic RAID parameter detection, the ability to rebuild arrays virtually, and support for a wide range of file systems. The software's user-friendly interface simplifies the recovery process, making it accessible even for those with limited technical expertise. By leveraging DiskInternals RAID Recovery™, businesses can effectively recover lost data, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuity in data accessibility.
Ready to get your data back?
To start recovering data from RAID 0, RAID 1, 0+1, 1+0, 1E, RAID 4, RAID 5, 50, 5EE, 5R, RAID 6, RAID 60, RAIDZ, RAIDZ2, and JBOD, press the FREE DOWNLOAD button to get the latest version of DiskInternals RAID Recovery® and begin the step-by-step recovery process. You can preview all recovered files absolutely for free. To check the current prices, please press the Get Prices button. If you need any assistance, please feel free to contact Technical Support. The team is here to help you with RAID 6 data recovery!
Best Practices for RAID 6 Configuration
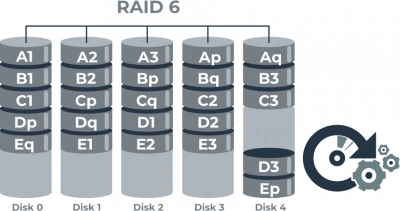
So, how to set up RAID 6? Effectively configuring and maintaining a RAID 6 system involves several best practices that maximize its reliability and performance. Implementing these strategies can help ensure continuous data protection and system resilience.
Implementing Hot Spares
One of the key strategies to enhance RAID 6 resilience is configuring hot spare drives. A hot spare is an unallocated drive that automatically takes the place of a failed drive. This precludes the need for immediate human intervention, allowing for automatic rebuilds and reducing downtime. By having hot spares on standby, RAID 6 systems can quickly recover from drive failures, maintaining data integrity and minimizing service disruptions.
Regular Data Backups
Despite RAID 6's inherent redundancy, maintaining up-to-date backups is essential. RAID configurations provide fault tolerance but are not immune to catastrophic failures or data corruption. Regular and reliable backups act as a safety net, ensuring data recovery even in worst-case scenarios. Effective backup management strategies include using automated backup solutions, maintaining offsite or cloud-based backups, and ensuring that backup schedules are adhered to consistently.
Monitoring System Health
Continuous monitoring of RAID array health is crucial for early detection of potential issues. Employing tools that provide real-time insights into drive health, array status, and performance metrics enables proactive management. Techniques such as SMART (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) analysis can detect anomalies early. Additionally, promptly responding to alerts and warnings is vital to prevent data loss and maintain system integrity. Implementing a robust monitoring framework ensures that any issues are addressed swiftly, preserving the longevity and reliability of the RAID 6 array.
Conclusion
RAID 6 stands out as a highly reliable data storage configuration, offering impressive fault tolerance through its dual parity system. With its capacity to endure up to two simultaneous drive failures, RAID 6 provides a robust solution for environments where data integrity is paramount. However, maximizing its potential requires more than just an understanding of its architecture. By adopting best practices such as implementing hot spares, maintaining regular data backups, and engaging in vigilant monitoring, organizations can enhance their RAID 6 systems' resilience and longevity. These strategies not only safeguard against potential failures but also ensure the continuous availability of critical data.
As technology evolves, tools like DiskInternals RAID Recovery™ further empower users to recover from unforeseen data loss with ease. By combining cutting-edge software solutions with proactive maintenance and management practices, RAID 6 remains a cornerstone for reliable data storage, balancing performance and protection in a world increasingly reliant on digital data.
