Manage Hyper-V Integration Services
Here you will find out:
- what are Hyper-V integrated services
- how to manage integrated services
- when DiskInternals can help you
Are you ready? Let's read!
What are Hyper-V integrated services?
Hyper-V integrated services are a whole range of services for modernized integration of a host server and a virtual machine in a virtual environment. The services offered are very diverse: some of them are only aimed at improving productivity, while others provide most of the functionality of the VM.
Hyper-V Integration Services represent a software suite of services which, when enabled, improves the integration between a host server and a VM in a virtual environment. Each Hyper-V service has a specific function aimed at enhancing the performance of guest operating systems.
Here are the main services provided by Hyper-V integrated services:
- Safe system shutdown, which involves shutting down the guest OS in a virtual machine from the management console. It automatically shuts down running applications and programs and saves the necessary files.
- Time synchronization between the virtual machine and the host server. This occurs when operations are performed in the same environment.
- Hyper-V key/value exchange between the virtual machine and its Hyper-V host.
- Heartbeat, a service that checks the correct loading of the VM and its condition in general.
- Volume Shadow Copy, which allows you to back up the necessary data of a running virtual machine to a single file (image) without disturbing the production environment.
- Guest Services, which enables you to copy files from a Hyper-V host to a running virtual machine, and vice versa. This service does not work by default; it needs to be activated in advance.
How to Manage Hyper-V Integration Services
Because it required to be manually deployed and updated on each guest OS, administering Hyper-V services used to be a difficult effort. With the exception of Guest Services, Hyper-V Integration Services are enabled by default in recent versions of the Windows operating system, and the necessary upgrades may be downloaded and installed automatically using Windows Update. Furthermore, by running PowerShell cmdlets or using Hyper-V Manager, you may quickly turn them on and off as needed. For proper communication between a Hyper-V host and a guest OS, be sure that each Hyper-V integration service is enabled and updated in both.
In order to assure proper operation, Hyper-V integration services must be enabled on both the Hyper-V host and the guest OS.
For this procedure, there are many possibilities as well:
- 1. Type "Services" and hit Enter in the Start menu's search box. The service that you wish to enable or stop may then be found under the Hyper-V Integration Service. Click OK after choosing the right action.
- 2. PowerShell can also be used with administrator rights. The main directive is: “Get-Service -Name VM*”.
- 3. Next, type "Start-Service" or "Stop-Service" depending on what you want to perform. "Stop-Service -Name VM*," for instance.
How to check the status and version of a Hyper-V integration service
Open PowerShell as an Administrator and run the following cmdlet to find out which Hyper-V integration services are active on the chosen VM:
Get-VMIntegrationService -VMName "TestVM"
You ought to see the following display if everything is in order:
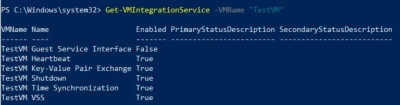
As you can see, all services have default activation set to on, with the exception of Hyper-V Guest Service Interface.
Additionally, check to see if all of the Hyper-V integration services on your guest VMs are current, since this might impact their performance in the future. Run this cmdlet to determine the guest's integration services version:
REG QUERY "HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Virtual Machine\Auto" /v IntegrationServicesVersion
How to turn on/off Hyper-V integrated services
There are two ways to control Hyper-V integrated services:
- 1. Using certain commands:
To enable Hyper-V guest services, you need to run PowerShell an enter:
Enable-VMIntegrationService -VMName "TestVM" -Name "Guest Service command Interface ".
To turn off, enter the command Disable-VMIntegrationService -VMName "TestVM" -Name "Guest Service Interface".
- 2. Using Hyper-V Manager Having selected the necessary VM in the central panel, right-click on it and select Settings from the list.
Next, you will need the “Management” section, where left-click on “Integration Services”. All possible integration services will be displayed here, indicating whether the host can use them in the virtual machine.
Turn an integration service on or off using PowerShell
You can use PowerShell to turn an integration service on or off in Hyper-V. Here are the general steps:
1. Open PowerShell: Press the Windows key and type "PowerShell" in the search bar. Right-click on "Windows PowerShell" and select "Run as administrator" to launch PowerShell with administrative privileges.
2. Check the integration services: Use the following command to view the integration services installed on your virtual machine:
Get-VMIntegrationService -VMName "YourVMName"
Replace "YourVMName" with the name of your virtual machine.
3. Turn the integration service on or off: Use the following command to turn an integration service on or off:
Set-VMIntegrationService -VMName "YourVMName" -Name "YourServiceName" -Enabled $True/$False
Replace "YourVMName" with the name of your virtual machine and "YourServiceName" with the name of the integration service that you want to turn on or off. Set the value of "-Enabled" to $True to turn the service on or $False to turn it off.
For example, to turn off the "Time Synchronization" integration service on a virtual machine named "VM1", you would use the following command:
Set-VMIntegrationService -VMName "VM1" -Name "Time Synchronization" -Enabled $False
4. Verify the change: Use the "Get-VMIntegrationService" command again to verify that the integration service is now enabled or disabled as desired.
These are the general steps to turn an integration service on or off using PowerShell. However, the specific syntax and options may vary depending on your version of PowerShell and the integration service that you are working with.
How to detect outdated Hyper-V integrated services
This can be done in one of the following three ways:
- 1. Using Hyper-V Dispatcher to check for outdated integration services is the easiest way. To get started, go into Hyper-V Manager and select the host to check which one the virtual machine belongs to. In the lower section in the central panel, all the information you are interested in will be displayed (this is the title of Integration Services).
- 2. Using Event Viewer, it is also easy to check for outdated integration services. Go to the Hyper-V-Integration organizational unit and select “Application and Service Logs”. Next, click on “Microsoft”, then “Windows”, then “Hyper-V Integration”. Now click “Administrator” and pay attention to the events with codes 4000 or 4010. If these codes are present, then the services are definitely outdated.
- 3. You can also use PowerShell and run the command: “Get-VM | select VMName, IntegrationServices State”. If the status of services is not reported to you, then the VM is either turned off or is under Linux.
How to start/stop a Hyper-V integration service
A Hyper-V integration service must be enabled on both the guest OS and the Hyper-V host, as was already discussed before, to guarantee effective performance. Generally speaking, the appropriate service within the guest OS begins or stops automatically when the service is started or stopped from a Hyper-V host. For instance, the chosen service will not execute if you start a Hyper-V integration service in the guest OS while it is deactivated in the Hyper-V host. Alternatively, if the service is halted in the guest OS while it is enabled in a Hyper-V host, Hyper-V will start it immediately. A Hyper-V host cannot launch the Hyper-V integration service if it is deactivated in the guest OS.
Follow these procedures to start or terminate a Windows-based Hyper-V integration service:
1. The search box below will open a related Windows program when you type Services.
2. Choose the service you wish to start or stop from a list of all Hyper-V integration services. You may see a brief summary of the service along with the setup choices in the left pane.
3. Choose the action to take by selecting with the right click the desired service.
A Hyper-V integration service may also be started or stopped using PowerShell. Follow these steps to achieve that:
1. Launch PowerShell as an administrator, type the following command to get a complete list of Hyper-V integration services active on the guest OS:
Get-Service -Name vm*
2. Use the Start-Service or Stop-Service cmdlets to start or stop the service running as a Windows guest. Look at the illustration below:
Stop-Service -Name "vmicshutdown"
Installing Hyper-V Integration Services for Linux Distributions that Do Not Ship with LIS Drivers and Services
In the following situations, you might need to install Hyper-V Integration Services in a Linux distribution:
- Linux distributions that don't come pre-integrated with LIS
- When LIS is updated and made available on the Microsoft website. Version 4.0 of Hyper-V Linux Integration Services is currently available.
The LIS ISO contains the necessary RPM files to aid in installing or updating the existing LIS components because Linux can only read RPM files for installation.
A Tar file (lis4-0-11.tar.gz) that can be sent to the target Linux virtual machine or an ISO file (lis4-0-11.iso) that may be attached to the Linux virtual machine are the two forms in which Hyper-V LIS 4.0 is offered. By supplying the ISO file, we'll walk you through installing LIS 4.0. (Note: The LIS 3.5 edition of Hyper-V Integration Services only came with an ISO file.)
The first step in installing LIS is to attach the LIS ISO to a virtual machine using Hyper-V Manager. Following that, run the commands listed below to complete the installation:
- 1. Connect a Linux virtual machine to the LinuxICv35.ISO file.
- 2. Use the following command to mount the ISO file as the root user: /dev/cdrom / media mount
- 3. Next, launch the LIS installation script provided with the LIS ISO by typing./install.sh.
- 4. Finally, you must restart the Linux virtual system in order for the Hyper-V LIS components to successfully initialize and register. Press enter after typing "reboot" in the terminal to restart the computer.
As described in the section of this article titled "Verifying Hyper-V LIS 4.0 Services and Drivers," after a reboot, use the "lsmod" or "Modinfo" command to examine the status of the LIS drivers and services.
Tip: Discover the difference between Hyper-V and VMware!Upgrading Hyper-V Linux Integration Services
The Hyper-V LIS drivers for Linux distributions can be updated using upgrade scripts that Microsoft has made available. Please follow the instructions above to mount the ISO file, and after switching to the directory appropriate for your Linux distribution, run the "Upgrade.sh" script.
Reboot the virtual machine after the script has finished installing the LIS drivers and services so that the Hyper-V LIS drivers and services may be registered with the Linux kernel.
Verifying Hyper-V Linux Integration Services 4.0 Services and Drivers
When LIS 4.0 has been updated or installed on a Linux virtual machine, you can use the command line to check if the LIS drivers and services have been registered:
lsmod OR lsmod | grep hv
The above command should list the Hyper-V LIS drivers and services. You’ll need to look for hid_hyperv, hv_netvsc, hv_utils, hv_storvsc and hv_vmbus for the successful activation of LIS.
If your VM is in danger
If your VM is in danger, or important files are already gone or damaged, then you need a professional application for recovering VMDK files. The best such application at the moment is DiskInternals VMFS Recovery. This application performs high-quality file recovery in real time without needing to turn off the VM.
Before buying a license, you will be able to view the files found for free; this must be done to verify the integrity of the files.
Also read and take note of the instructions for working with DiskInternals VMFS Recovery:
Download DiskInternals VMFS Recovery and install the program, so you can proceed to recover the VM files.
Connect via SSH, if necessary, and then open the disk (it can be a local disk or SSH).
Next begin scanning; the search results will soon appear on the screen.
Now find the necessary VMDK files and mount them.
Open the mounted VMDK file by double-clicking the left mouse button and view all the files. This is necessary to verify their integrity.
The last stage is buying a license and the completion of data export to an alternative information storage device.
FAQ
Can I disable Hyper-V services?
Yes, you can disable Hyper-V services if you no longer need to use them. Here are the steps to disable Hyper-V services in Windows 10:
1. Press the Windows key + X and select "Apps and Features" from the menu.
2. In the "Apps and Features" window, click on "Programs and Features" on the right-hand side.
3. In the "Programs and Features" window, click on "Turn Windows features on or off" from the left-hand side.
4. In the "Windows Features" window, find and uncheck the box next to "Hyper-V".
5. Click "OK" to save the changes.
6. Wait for the changes to take effect and then restart your computer.
Once you have disabled Hyper-V services, you will no longer be able to use Hyper-V virtualization features on your computer. If you need to use Hyper-V in the future, you can follow the same steps and re-enable the Hyper-V feature by checking the box next to "Hyper-V" in the "Windows Features" window.
What is Hyper-V and do I need it?
Hyper-V is a virtualization technology developed by Microsoft that allows you to create and run virtual machines on a Windows computer. It enables you to run multiple operating systems on a single physical machine, allowing you to use different software and applications without the need for multiple physical computers.
Hyper-V is primarily used by IT professionals and developers for testing, development, and server consolidation purposes. It can also be used by home users who need to run multiple operating systems on a single computer for various reasons.
If you are not an IT professional or a developer and do not have a specific need for running virtual machines, you may not need Hyper-V.
Should I disable Hyper-V services?
Whether or not to disable Hyper-V services depends on your specific use case and needs.
Hyper-V is a virtualization technology that allows you to create and manage virtual machines on your Windows operating system. If you are using Hyper-V to run virtual machines, then disabling the Hyper-V services would prevent you from doing so.
On the other hand, if you are not using Hyper-V and do not plan to use it in the future, disabling the services can free up system resources and improve overall performance. Disabling Hyper-V can also be necessary if you are using other virtualization software that is incompatible with Hyper-V.
How do I run a Hyper-V service?
Here are the general steps to create and run a virtual machine using Hyper-V:
- Open the Hyper-V Manager: You can find this by typing "Hyper-V" in the Start menu or by using the search function.
- Create a virtual machine: Click on the "New" button in the Actions pane or right-click on your server name and choose "New" -> "Virtual Machine." Follow the prompts to configure the virtual machine's settings, such as the name, location, memory, and hard disk space.
- Install the operating system: Once the virtual machine is created, you need to install an operating system. This can be done by attaching an ISO file containing the operating system installation media to the virtual machine's DVD drive or by using a physical installation media.
- Start the virtual machine: Once the operating system is installed, you can start the virtual machine by selecting it in the Hyper-V Manager and clicking the "Start" button. This will launch the virtual machine in its own window.
- Access the virtual machine: To access the virtual machine, you can either connect to it using a remote desktop connection or by using the console window provided by Hyper-V.
These are the basic steps to create and run a virtual machine using Hyper-V. However, it's important to note that the process may vary depending on your specific needs and requirements.
