VMware NFS vs VMFS comparison: features and benefits

This article is dedicated to VMware NFS vs VMFS comparison.
Here you will find out:
- how VMFS differs from NFS
- VMware VMFS vs NFS datastores: differences and benefits
- when DiskInternals can help you
Read it to find out all that you need!
Storage types at the ESXi logical level: VMware VMFS vs NFS
NFS operates at the file level as a network file system, whereas VMFS functions at the block level as a virtual machine file system. Alongside NFS and VMFS, VMware can also utilize vSAN and VVols as varying types of datastores. Within a virtual machine's logical framework, there exist multiple fundamental storage categorizations:
- Thick Provision Eager Zeroed: This format entails a complete allocation and zeroing of the disk space upon creation, a process that is both time and resource-intensive. The allocated space is exclusively reserved, rendering it inaccessible for use by other VMs.
- Thick Provision Lazy Zeroed: Similar to the eager zeroed type, this method allocates all necessary space during the setup but leaves the data that previously occupied the space unchanged (stale) until it's explicitly zeroed. When data is written to a new block, the system needs to overwrite any existing data with zeros first, which can elevate the input/output operations per second (IOPS) required for these blocks. Like its eager counterpart, the reserved disk space is not available for other VMs.
- Thin Provision: Contrary to the thick formats, thin provisioning dynamically allocates and zeros disk space as it is needed, rather than upfront. This approach allows for efficient space utilization, as unused disk space remains available for other virtual machines to leverage.
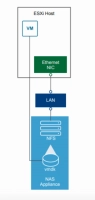
Network File System (NFS) in VMware
NFS, as mentioned above, is a network file system that was originally created only for UNIX systems. The NFS client embedded in a ESXi host uses the NFS protocol over TCP / IP to operate a designated NFS volume located on the NAS. An ESXi host can mount an NFS volume and then use it for its storage needs. VSphere supports multiple versions of NFS versions: 3 and 4.1.
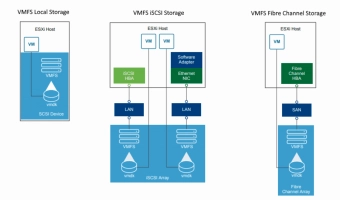
Virtual Machine File System (VMFS) in VMware
VMware uses VMFS to store virtual machines as well as snapshots. VMFS is the most suitable cluster file system for virtualization. It can be shared by multiple ESXi hosts and virtual machines. With it, you can simultaneously write and read data in one storage location and vice versa. VMFS-based datastores use the native vSphere Virtual Machine File System (VMFS) format, which is optimized for storing virtual machines.
VMware VMFS vs NFS datastores: differences and benefits
These file systems immediately differ in their level of utilization: VMFS is at the block level and NFS is at the file level.
The VMFS datastore is created by vSphere, while the NFS file system is created on the storage side and mounted with only the shared folder on vSphere. You should choose NFS when you need to use CIFS shared folders. In other cases, it is better to choose VMFS in order to avoid possible limitations in the VMware environment.
Protecting your data is possible with VMFS Recovery
If NFS or VMFS does not work and you need to recover data from storage, use VMFS Recovery. This app allows you to recover data from any inaccessible or damaged disks in automatic mode, thanks to the Recovery Wizard. The recovered information is exported to local or remote locations (including FTP), and any virtual disk can be converted to local for access (for example, in Windows Explorer). Another useful and accessible feature is Unicode support. Learn more about how to reset VMWare virtual machine and VMware Workstation vs VirtualBox recovery here!
Check out these instructions on how to use DiskInternals VMFS Recovery:
- Download this app from the DiskInternals website for Windows Vista, 7, 8, and 10 or Windows Server 2006-2019.
- After launching the application, connect via SSH, if necessary. Open the disk and start scanning.
- After this, VMFS Recovery will find all VMDK files and mount them.
- Then check the recovered files for their integrity.
- If everything suits you, it's time to buy a license and export all found or certain files at your discretion.