What exactly is VMware Remote Console and how Use it in Linux and Windows?
There are many ways to manage your VMware virtual machines and ESXi hosts; you could use the web UI instance, which is accessible on web browsers, or install the standalone Remote Console client. The remote console app fosters access to VMs on a remote host, but you can only launch this client app from vSphere.
So, what exactly is the VMware Remote Console (VMRC) client and how does it run for managing vSphere appliances? This article details everything you should know about this topic, with the inclusion of how to uninstall the console when you feel you’re done with it. The VMRC can run on Windows and Linux operating systems.
What Is VMware Console?
Contrary to the VMware Remote Console (take note of the “Remote” inclusion), the VMware Console is a web UI application for accessing your guest OSes deployed on VMware vSphere VMs. Older versions of vSphere used a standalone vSphere Client application (written on C#) for managing ESXi hosts, VMs, and guest OSes.
Starting with vSphere 6.x, VMware launched an HTML 5 vSphere Client and VMware Host Client to offer a web UI for managing vSphere resources; this UI became the default option for accessing vSphere resources. However, there is an alternative management tool, the VMware Remote Console, which is a standalone application that allows for connecting to remote hosts.
Tip: how to install VMware tools on UbuntuWhat Is VMware Remote Console
Put simply, the VMware Remote Console (VMRC) client is a separate entity that integrates remote console access functionality to the vSphere Web Client. When installed, vSphere admins can access and manage VMs or ESXi hosts in other clients.
Although VMRC is standalone, you can only launch it from within the vSphere web client. It does not create a shortcut or app icon on your desktop after the installation, and you can't launch it directly from the Program Files folder.
If you install the VMRC and find it to not be interesting, you can uninstall it and install VMware Fusion Pro (for macOS only) or Workstation (Windows and Linux); the VMRC is entirely free and works on all three mainstream OSes: Windows, Linux, macOS.
Main Features of VMRC
The main feature offered by VMRC is the remote access functionality it adds to the vSphere web client. However, when launched, you can access a number of remote host management – allowing you to edit the VM settings of virtual machines on a remote host.
Through VMRC, you can add or manage memory, virtual processors, virtual disks, CD/DVD drives, virtual floppy drives, manage virtual network adapters, insert ISO images into CD/DVD drives, and perform other actions on a remote VM. Some notable features include:
- USB Passthrough: You can connect a removable device to your local machine and access it on the remote VM you’re connected to via VMware Remote Console.
- Proxy Support: VMRC supports proxy in network configurations for accessing ESXi hosts and VMs.
- Supports VMware Tools: You can initiate VMware Tools installation from VMware Remote Console.
- Resolution Adjustment: VMRC can adjust to the resolution of the guest OS you’re working on.
Downloading VMware Remote Console
You need to be logged into your VMware account to be able to download VMRC for your native OS. The Windows OS installer file comes in ZIP format, you have to extract it and install the EXE file. The Linux OS install comes as a .bundle file, while the macOS version can be gotten from the Apple macOS Store.
How to Install VMRC on Linux?
This is a guide to installing VMRC on the Ubuntu Linux distro. To achieve this, you must first install the libaio1 package on your Ubuntu system (if it’s not already installed previously). Here’s the command to install libaio1:
- sudo apt-get install libaio1
Now go to the file directory where you saved the Linux installer file of VMware Remote Console and make some edits in this manner. This permissions edit is because VMRC is not available on Linux repos.
- sudo chmod +x ./VMware-Remote-Console-12.0.0-17287072.x86_64.bundle
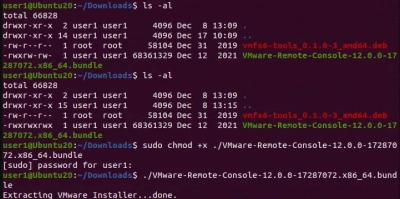
When you have set the permissions, you can now run the installer file to install VMRC on Ubuntu.
- sudo ./VMware-Remote-Console-12.0.0-17287072.x86_64.bundle
At this point, the GUI VMRC installer screen will pop up and you can follow the installation wizard to set your installation options. Once the product is successfully installed, close the installer window – you can now launch VMRC, but not directly, remember.
How to Launch VMware Remote Console in Linux
The only way to launch VMRC is through VMware vSphere Client or VMware Host Client; you have to click a link to launch the app.
- Log in to vSphere Client or VMware Host Client and go to the navigator pane.
- Click on the Virtual Machines tab and select the VM you want to connect to remotely.
- Now, click on the PC monitor icon (with a green arrow) to open a context menu – select “Launch Remote Console” from the options to open VMRC.
- You will be prompted to select an application for opening VMRC links, VMware Remote Console should be selected by default since it is already installed on your system, but if not, click on the “Choose..” button and select it. (Check the box beside “always use this application to open VRMC links).
- Click on “Open Link” and choose “Connect Anyway” in the prompt that will appear.
- Your guest OS will launch in VMRC and you can manage the VM or edit the settings you wish to change.
How to Install VMRC on Windows
Unlike in Linux, installing VMRC on Windows is quite straightforward and follows a similar process as with installing any other software. Hereunder are the steps to install VMware Remote Console on a Windows computer.
- Unpack the ZIP installer package and look for the .exe installer file
- Double-click the installer file to launch the installation wizard (you need Admin rights on the PC)
- Follow the wizard prompts to set your installation preferences and complete the process.
- You will need to reboot the computer after installing VMRC on Windows OS.
- After the system reboots, to launch VMRC, you need to first log in to vSphere Host Client or vCenter.
How to Launch VMware Remote Console in Windows
- Open vCenter on your preferred web browser and log in with your credentials
- Launch VMware vSphere Client and log in
- Now, go to Host and Clusters 🡺 select the VM you want to access remotely 🡺 click on the Launch Remote Console link.
- You will be prompted to choose an application for opening VRMC links (just like in Linux), select the VMware Remote Control app you have just installed, and check the box beside “Always use this application to open VMRC links.”
- Click the “Open Link” button to launch the selected VM in the Remote Console.
If you want Remote Console to be your preferred interface, change the settings from the account preferences page.
- Click on your account name at the top right corner and select My Preferences.
- Toggle to the Default Console tab and select VMware Remote Console (VMRC)
- Save the settings and exit.
Interface and Options of VMware Remote Console
The VMRC interface has numerous features to play with; these features are well-arranged on the menu options for easy access. You can shut down a VM, access removable devices on the primary system, and set preferences for the VM you’re accessing – all from the VMRC menu options. There is also a “Help” page that displays many handy troubleshooting options for VMRC, in case you get stuck.
Tip: learn more about VMware, reset virtual machine, update and recover it!Advanced VMRC Configuration Parameters
- The log file location in Windows is at: LOCALAPPDATA\temp\vmware-%USERNAME% folder.
- Log files in Linux: TEMP/vmware-%USERNAME%/
- USB Arbitrator log: /tmp/VMware-root/
- Set VMRC as your default app if you have VMware Workstation installed in Windows:
- Open PowerShell and run this command:
- Get-Item “HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Classes\vmrc\DefaultIcon”
- Get-Item “HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Classes\vmrc\shell\open\command”
- Set-Item HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Classes\vmrc\DefaultIcon -Value ‘”C:\Program Files (x86)\VMware\VMware Remote Console\vmrc.exe”,0’
- Set-Item HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Classes\vmrc\shell\open\command -Value ‘”C:\Program Files (x86)\VMware\VMware Remote Console\vmrc.exe” “%1″‘
How to Log Out of VMware Remote Console
By pressing the CTRL+ALT keys, you will exit the VMRC mode and return to vCenter vSphere Client. You can log out by clicking the Menu option and selecting the “Exit” link.
Uninstalling VMware Remote Console
If for any reason, you need to uninstall the VMRC from your Linux or Windows, hereunder are the procedures to follow.
Linux
- View all VMware products installed on your Linux system: VMware-installer -l
- Uninstall VMRC: vmware-installer –uninstall-product vmware-vmrc
If VMRC doesn’t uninstall, here’s how to forcefully remove it:
- Open /etc/vmware-installer/database in DB Explorer for SQLite
- Locate the component_dependencies table
- Delete any row with this info: vmware-usbarbitrator>=17.1.1.
Windows
- Open Windows Control Panel and go to Programs and Features
Find VMware Remote Console, click on it, and select “Uninstall.”
Tip: learn more about VMware data recovery!Conclusion
Summarily, VMware Remote Console is a useful application for accessing VMs and guest OSes remotely from the vSphere client. It has a GUI interface that is easy to understand and comes with a suite of features. Installing the VMRC app on Linux and Windows is quite simple and you can uninstall it at any time.
FAQ
What is VMware remote console used for?
VMware Remote Console enables the management of virtual machines on distant hosts by allowing console and device activities, including the adjustment of operating system configurations and monitoring the VM console within VMware vSphere. Additionally, it allows for the modification of virtual machine configurations, such as memory (RAM), processor cores, and storage disks.
How do I open the remote console in VMware?
Within the vSphere Client, locate a virtual machine from the inventory. Then, on the Summary tab, select Launch Remote Console.
How do I access VMware Web client?
Alternatively, launch a Web browser and navigate to the vSphere Client URL: https://vcenter_server_ip_address_or_fqdn/ui. Should a warning about potential security risks pop up, choose to proceed to the website. On the vSphere Welcome page, click on Launch vSphere Client (HTML5).
Where is browser console in ESXi?
To open the ESXI Console Screen press ALT + F1.
How do I access the VM console?
Sign in to the VMware Cloud Console via https://vmc.vmware.com. Optionally, you may need to set up a management gateway firewall rule allowing access to ESXi through port 443, necessary only if you're connecting to VMRC via a VPN. Next, in the vSphere Client, choose the virtual machine you wish to access using VMRC and click on LAUNCH REMOTE CONSOLE.
