How to run a shell script in the background
Here you will find out:
- when you may run a command in the background
- how to use &, nohups and the SCREEN command
- when DiskInternals can help you
Are you ready? Let's read!
When you may run a command in the background
If commands are executed in the foreground, this may become inconvenient for you. A command can take a long time until it completes, during which time you cannot set a new command. In this case, working at a computer can be complicated and time-consuming. In order to avoid such situations and to increase user comfort, you can run a bash script in the background. That is, the task can be scheduled to run from the terminal without user intervention. This way, you free up your time and improve your computer’s functioning.
Using & at the end of the command
Putting a command in the background is extremely simple, you only need one character: &.
Here’s an example:
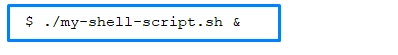
After that, you can continue to use the terminal without waiting for the end of the session. If the terminal session is closed, the command ends and the background command is turned off automatically. If this does not suit you, and you want the task to continue in the background on an ongoing basis, then this can also be done. To do this, you must first enter “&”, and then the DISOWN command.
Here's what it looks like in an example:

To verify the correctness of the actions, you can enter the JOBS command.
Now you know that making running a background task is easy!
Using nohups
If you want to run a task in background mode for a long time, then you should use the NOHUP command. For example:
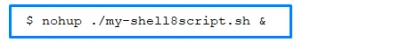
This command weakens the HUP signal as much as possible, as a result of which it is possible to execute commands in the background when the terminal is off.
Using the SCREEN command
Using NOHUP and &, the command in the background will be executed even after logging out. However, this does not mean that you can connect to the same session again to see exactly what is happening on the screen. There is an onscreen command for this. With its help, Linux suggests disconnecting the session on which a process is running. This command weakens the HUP signal as much as possible, as a result of which it is possible to run a script in the background with the terminal turned off.
If you want to get files from Linux
If you are using a dual-boot installation or a virtual machine, and you need to get files from Linux to Windows, you must install a one-of-a-kind application: DiskInternals Linux Reader. This program makes it possible to get absolutely any files in Windows from Linux for free. When there is such an opportunity, you should use it. The application works with many file systems (Ext2 / Ext3 / Ext4, HFS, ReiserFS, and others). Access is available to all files as read-only on Linux disks (the source files will be unchanged in any case). The program reads any kind of drive: SSDs, memory cards, HDDs, flash drives and others. Creating a disk image is an unrivaled bonus for customers.